Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), or (formerly) fibrosing alveolitis, is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic
 In many people, symptoms are present for a considerable time before diagnosis. The most common clinical features of IPF include the following:
* Age over 50 years
* Dry, non-productive cough on exertion
* Progressive exertional dyspnea (shortness of breath with exercise)
* Dry, inspiratory bibasilar "velcro-like"
In many people, symptoms are present for a considerable time before diagnosis. The most common clinical features of IPF include the following:
* Age over 50 years
* Dry, non-productive cough on exertion
* Progressive exertional dyspnea (shortness of breath with exercise)
* Dry, inspiratory bibasilar "velcro-like"
 Despite extensive investigation, the cause of IPF remains unknown. The
Despite extensive investigation, the cause of IPF remains unknown. The
www.diagnoseipf.com
. The key issue facing clinicians is whether the presenting history,
 Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) belongs to a large group of more than 200 lung diseases known as
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) belongs to a large group of more than 200 lung diseases known as
 The radiological evaluation through HRCT is an essential point in the diagnostic pathway in IPF. HRCT is performed using a conventional computed axial tomographic scanner without injection of contrast agents. Evaluation slices are very thin, 1–2 mm.
Typical HRCT of the chest of IPF demonstrates fibrotic changes in both lungs, with a predilection for the bases and the periphery. According to the joint ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT 2011 guidelines, HRCT is an essential component of the diagnostic pathway in IPF which can identify UIP by the presence of:
* Reticular opacities, often associated with traction bronchiectasis
*
The radiological evaluation through HRCT is an essential point in the diagnostic pathway in IPF. HRCT is performed using a conventional computed axial tomographic scanner without injection of contrast agents. Evaluation slices are very thin, 1–2 mm.
Typical HRCT of the chest of IPF demonstrates fibrotic changes in both lungs, with a predilection for the bases and the periphery. According to the joint ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT 2011 guidelines, HRCT is an essential component of the diagnostic pathway in IPF which can identify UIP by the presence of:
* Reticular opacities, often associated with traction bronchiectasis
* 

 The clinical course of IPF can be unpredictable. IPF progression is associated with an estimated median survival time of 2 to 5 years following diagnosis.
The 5-year survival for IPF ranges between 20 and 40%, a mortality rate higher than that of a number of malignancies, including colon cancer, multiple myeloma and bladder cancer.
Recently a multidimensional index and staging system has been proposed to predict mortality in IPF. The name of the index is GAP and is based on gender age and two lung physiology variables (FVC and DLCO that are commonly measured in clinical practice to predict mortality in IPF. The highest stage of GAP (stage III) has been found to be associated with a 39% risk of mortality at 1 year. This model has also been evaluated in IPF and other ILDs and shown good performance in predicting mortality in all main ILD subtypes. A modified ILD-GAP Index has been developed for application across ILD subtypes to provide disease-specific survival estimates. In IPF patients, the overall mortality at 5 years rate is high but the annual rate of all-cause mortality in patients with mild to moderate lung impairment is relatively low. This is the reason why change in lung function (FVC) is usually measured in 1-year clinical trials of IPF treatments rather than survival.
In addition to clinical and physiological parameters to predict how rapidly patients with IPF might progress, genetic and molecular features are also associated with IPF mortality. For example, it has been shown that IPF patients who have a specific genotype in the mucin MUC5B gene polymorphism (see above) experience slower decline in FVC and significantly improved survival. Even if such data are interesting from a scientific point of view, the application in the clinical routine of a prognostic model based on specific genotypes is still not possible.
The clinical course of IPF can be unpredictable. IPF progression is associated with an estimated median survival time of 2 to 5 years following diagnosis.
The 5-year survival for IPF ranges between 20 and 40%, a mortality rate higher than that of a number of malignancies, including colon cancer, multiple myeloma and bladder cancer.
Recently a multidimensional index and staging system has been proposed to predict mortality in IPF. The name of the index is GAP and is based on gender age and two lung physiology variables (FVC and DLCO that are commonly measured in clinical practice to predict mortality in IPF. The highest stage of GAP (stage III) has been found to be associated with a 39% risk of mortality at 1 year. This model has also been evaluated in IPF and other ILDs and shown good performance in predicting mortality in all main ILD subtypes. A modified ILD-GAP Index has been developed for application across ILD subtypes to provide disease-specific survival estimates. In IPF patients, the overall mortality at 5 years rate is high but the annual rate of all-cause mortality in patients with mild to moderate lung impairment is relatively low. This is the reason why change in lung function (FVC) is usually measured in 1-year clinical trials of IPF treatments rather than survival.
In addition to clinical and physiological parameters to predict how rapidly patients with IPF might progress, genetic and molecular features are also associated with IPF mortality. For example, it has been shown that IPF patients who have a specific genotype in the mucin MUC5B gene polymorphism (see above) experience slower decline in FVC and significantly improved survival. Even if such data are interesting from a scientific point of view, the application in the clinical routine of a prognostic model based on specific genotypes is still not possible.
scarring
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a na ...
lung disease
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
function. The tissue in the lungs becomes thick and stiff, which affects the tissue that surrounds the air sacs in the lungs. Symptoms typically include gradual onset of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing disc ...
and a dry cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three pha ...
. Other changes may include feeling tired, and abnormally large and dome shaped finger and toenails (nail clubbing). Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
, pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
or pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain p ...
.
The cause is unknown, hence the term idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent wikt:spontaneous, spontaneous origin. From Ancient Greek, Greek ἴδιος ''idios'' "one's own" and πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", ''idiopathy'' means approxi ...
. Risk factors include cigarette smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or simply released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed ...
, acid reflux disease (GERD), certain viral infection
A viral disease (or viral infection) occurs when an organism's body is invaded by pathogenic viruses, and infectious virus particles (virions) attach to and enter susceptible cells.
Structural Characteristics
Basic structural characteristics, s ...
s, and genetic predisposition. The underlying mechanism involves scarring of the lungs. Diagnosis requires ruling out other potential causes. It may be supported by a HRCT scan or lung biopsy
A lung biopsy is an interventional procedure performed to diagnose lung pathology by obtaining a small piece of lung which is examined under a microscope. Beyond microscopic examination for cellular morphology and architecture, special stains and ...
which show usual interstitial pneumonia
Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring (fibrosis) involves the pulmonary interstitium (the supporting framework of the lung). UIP is thus classified as a for ...
(UIP). It is a type of interstitial lung disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the alveoli (air sacs)) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmo ...
(ILD).
People often benefit from pulmonary rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation, also known as respiratory rehabilitation, is an important part of the management and health maintenance of people with chronic respiratory disease who remain symptomatic or continue to have decreased function despite stand ...
and supplemental oxygen
Oxygen therapy, also known as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as medical treatment. Acute indications for therapy include hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels), carbon monoxide toxicity and cluster headache. It may also be prophylactical ...
. Certain medications like pirfenidone (Esbriet) or nintedanib (Ofev) may slow the progression of the disease. Lung transplantation
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one lung lobe. ...
may also be an option.
About 5 million people are affected globally. The disease newly occurs in about 12 per 100,000 people per year. Those in their 60s and 70s are most commonly affected. Males are affected more often than females. Average life expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
following diagnosis is about four years. Updated international guidelines were published in 2022, which some simplification in diagnosis and the removal of antacids as a possible adjunct therapy.
Signs and symptoms
 In many people, symptoms are present for a considerable time before diagnosis. The most common clinical features of IPF include the following:
* Age over 50 years
* Dry, non-productive cough on exertion
* Progressive exertional dyspnea (shortness of breath with exercise)
* Dry, inspiratory bibasilar "velcro-like"
In many people, symptoms are present for a considerable time before diagnosis. The most common clinical features of IPF include the following:
* Age over 50 years
* Dry, non-productive cough on exertion
* Progressive exertional dyspnea (shortness of breath with exercise)
* Dry, inspiratory bibasilar "velcro-like" crackles
Crackles are the clicking, rattling, or crackling noises that may be made by one or both lungs of a human with a respiratory disease during inhalation. They are usually heard only with a stethoscope ("on auscultation"). Pulmonary crackles are a ...
on auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory and respiratory systems (hea ...
(a crackling sound in the lungs during inhalation similar to Velcro being torn apart slowly, heard with a stethoscope).
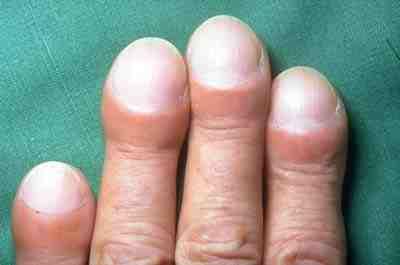
* Clubbing of the digits, a disfigurement of the finger tips or toes (see image)
* Abnormal pulmonary function test
Pulmonary function testing (PFT) is a complete evaluation of the respiratory system including patient history, physical examinations, and tests of pulmonary function. The primary purpose of pulmonary function testing is to identify the severity ...
results, with evidence of restriction and impaired gas exchange.
Some of these features are due to chronic hypoxemia
Hypoxemia is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia has many causes, and often causes hypoxia as the blood is not supplying enough oxygen to the tissues of the body ...
(oxygen deficiency in the blood), are not specific for IPF, and can occur in other pulmonary disorders. IPF should be considered in all patients with unexplained chronic exertional dyspnea who present with cough, inspiratory bibasilar crackles, or finger clubbing.
Assessment of "velcro" crackles on lung auscultation is a practical way to improve the earlier diagnosis of IPF. Fine crackles are easily recognized by clinicians and are characteristic of IPF.
If bilateral fine crackles are present throughout the inspiratory time and are persisting after several deep breaths, and if remaining present on several occasions several weeks apart in a subject aged ≥60 years, this should raise the suspicion of IPF and lead to consideration of an HRCT scan of the chest which is more sensitive than a chest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
. As crackles are not specific for IPF, they must prompt a thorough diagnostic process.
Causes
The cause of IPF is unknown but certain environmental factors and exposures have been shown to increase the risk of getting IPF.Cigarette smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice of burning tobacco and ingesting the resulting smoke. The smoke may be inhaled, as is done with cigarettes, or simply released from the mouth, as is generally done with pipes and cigars. The practice is believed ...
is the best recognized and most accepted risk factor for IPF, and increases the risk of IPF by about twofold. Other environmental and occupation exposures such as exposure to metal dust, wood dust, coal dust, silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
, stone dust, biologic dusts coming from hay dust or mold spores or other agricultural products, and occupations related to farming/livestock have also been shown to increase the risk for IPF. There is some evidence that viral infections may be associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and other fibrotic lung diseases.
Pathogenesis
 Despite extensive investigation, the cause of IPF remains unknown. The
Despite extensive investigation, the cause of IPF remains unknown. The fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is a pathological wound healing in which connective tissue replaces normal parenchymal tissue to the extent that it goes unchecked, leading to considerable tissue remodelling and the formation of perma ...
in IPF has been linked to cigarette smoking, environmental factors (e.g. occupational exposure to gases, smoke, chemicals or dusts), other medical conditions including gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/ ...
(GERD), or to genetic predisposition (familial IPF). However, none of these is present in all people with IPF and therefore do not provide a completely satisfactory explanation for the disease.
IPF is believed to be the result of an aberrant wound healing process including/involving abnormal and excessive deposition of collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole ...
(fibrosis) in the pulmonary interstitium with minimal associated inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
. Cellular senescence
Cellular senescence is a phenomenon characterized by the cessation of cell division. In their experiments during the early 1960s, Leonard Hayflick and Paul Moorhead found that normal human fetal fibroblasts in culture reach a maximum of approxi ...
is suspected to be a central contributing cause, a belief which is supported by benefits seen in patients given senolytic
A senolytic (from the words ''senescence'' and ''-lytic'', "destroying") is among a class of small molecules under basic research to determine if they can selectively induce death of senescent cells and improve health in humans. A goal of this ...
therapy.
It is hypothesized that the initial or repetitive injury in IPF occurs to the lung cells, called alveolar epithelial cells (AECs, pneumocytes), which line the majority of the alveolar surface. When type I AECs are damaged or lost, it is thought that type II AECs undergo proliferation to cover the exposed basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between Epithelium, epithelial tissues including mesot ...
s. In normal repair, the hyperplastic type II AECs die and the remaining cells spread and undergo a differentiation process to become type I AECs. Under pathologic conditions and in the presence of transforming growth factor beta
Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms (TGF-β 1 to 3, HGNC symbols TGFB1, TGFB2, TGFB3) and many other sign ...
(TGF-β), fibroblasts
A fibroblast is a type of biological cell that synthesizes the extracellular matrix and collagen, produces the structural framework ( stroma) for animal tissues, and plays a critical role in wound healing. Fibroblasts are the most common cells o ...
accumulate in these areas of damage and differentiate into myofibroblasts
A myofibroblast is a cell phenotype that was first described as being in a state between a fibroblast and a smooth muscle cell.
Structure
Myofibroblasts are contractile web-like fusiform cells that are identifiable by their expression of α-sm ...
that secrete collagen and other proteins. In the current classification of the pathogenesis of IPF, it is believed that it occurs by way of the formation of a UIP (usual interstitial pneumonia) lesion, which then undergoes the aforementioned pathological condition characteristic of IPF. Other proposed repeated injury mechanisms indicate that IPF may result not just from a UIP lesion, but also from NSIP and DAD (nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and diffuse alveolar damage) lesions, or a combination of several.
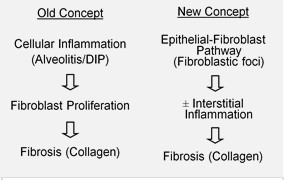
In the past, it was thought that inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
was the first event in initiating lung tissue scarring. Later findings showed that the development of fibroblastic foci precedes the accumulation of inflammatory cells and the consequent deposition of collagen. This pathogenetic model is indirectly supported by the clinical features of IPF, including an insidious onset over several years, relatively infrequent acute exacerbations, and failure to respond to immunosuppressive therapy
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse react ...
. However, it is the belief of some researchers that the disease is a multi-mechanistic one, wherein the trigger for the disease may stem from abnormalities in any number of wound healing pathways, including the inflammatory response. Such abnormalities could occur in any number of the nine implicated pathways (clotting cascade, antioxidant pathways, apoptosis, inflammatory cytokines, angiogenesis and vascular remodelling, growth factors, surfactant and matrix regulatory factors), and that through further investigation into all nine, novel therapies and approaches could be proposed on a unique or case-by-case basis should attempts at treating or circumventing complications in any one pathway prove unsuccessful. A number of therapies that target fibroblast activation or the synthesis of extracellular matrix are currently in early testing or are being considered for development.
Familial IPF accounts for less than 5% of the total of patients with IPF and is clinically and histologically indistinguishable from sporadic IPF. Genetic associations include mutations in pulmonary surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active complex of phospholipids and proteins formed by type II alveolar cells. The proteins and lipids that make up the surfactant have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is t ...
proteins A1, A2, C ( SFTPA1, SFTPA2B) and mucin
Mucins () are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins (glycoconjugates) produced by epithelial tissues in most animals. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in most ...
(MUC5B
Mucin-5B (MUC-5B) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MUC5B'' gene
and by ''Muc5b'' gene in mouse. It is one of the five gel-forming mucins. MUC-5B can be found in whole saliva, normal lung mucus, and cervical mucus. In some disease ...
).
A remarkable aspect of the MUC5B variant is its high frequency of detection, as it is found in approximately 20% of individuals with Northern and Western European ancestry and in 19% of the Framingham Heart Study population.
Mutations in human telomerase
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of the chromosomes of most euka ...
genes are also associated with familial pulmonary fibrosis and in some patients with sporadic IPF (e.g. the TERT
Telomerase reverse transcriptase (abbreviated to TERT, or hTERT in humans) is a catalytic subunit of the enzyme telomerase, which, together with the telomerase RNA component (TERC), comprises the most important unit of the telomerase complex.
T ...
, TERC genes). Recently an X-linked mutation in a third telomerase-associated gene, dyskerin (DKC1), has been described in a family with IPF.
Diagnosis
An earlier diagnosis of IPF is a prerequisite for earlier treatment and, potentially, improvement of the long-term clinical outcome of this progressive and ultimately fatal disease. If IPF is suspected, diagnosis can be challenging but a multidisciplinary approach involving a pulmonologist, radiologist and pathologist expert in interstitial lung disease has been shown to improve the accuracy of IPF diagnosis. A Multidisciplinary Consensus Statement on the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias published by theAmerican Thoracic Society The American Thoracic Society (ATS) is a nonprofit organization focused on improving care for pulmonary diseases, critical illnesses and sleep-related breathing disorders. It was established in 1905 as the
American Sanatorium Association, and ch ...
(ATS) and the European Respiratory Society
The European Respiratory Society, or ERS, is a non-profit organization with offices in Lausanne, Brussels and Sheffield. It was founded in 1990 in the field of respiratory medicine. The organization was formed with the merger of the Societas Euro ...
(ERS) in 2000 proposed specific major and minor criteria for establishing the diagnosis of IPF. However, in 2011, new simplified and updated criteria for the diagnosis and management of IPF were published by the ATS, ERS, together with the Japanese Respiratory Society (JRS) and Latin American Thoracic Association (ALAT). Currently, a diagnosis of IPF requires:
* Exclusion of known causes of ILD, e.g., domestic and occupational environmental exposures, connective tissue disorders, or drug exposure/toxicity
* The presence of a typical radiological pattern of usual interstitial pneumonia
Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) is a form of lung disease characterized by progressive scarring of both lungs. The scarring (fibrosis) involves the pulmonary interstitium (the supporting framework of the lung). UIP is thus classified as a for ...
(UIP) on high-resolution computed tomography
High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is a type of computed tomography (CT) with specific techniques to enhance image resolution. It is used in the diagnosis of various health problems, though most commonly for lung disease, by assessing t ...
(HRCT).
In the right clinical setting, it is possible to make the diagnosis of IPF by HRCT alone, obviating the need for surgical lung biopsy.
Various technologies using Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech re ...
have been developed to help with diagnosis. A deep learning algorithm for categorizing high-resolution CT images reported high accuracy and a research project led by Nagoya University
, abbreviated to or NU, is a Japanese national research university located in Chikusa-ku, Nagoya. It was the seventh Imperial University in Japan, one of the first five Designated National University and selected as a Top Type university of T ...
Graduate School of Medicine and Riken used a combination of Deep learning
Deep learning (also known as deep structured learning) is part of a broader family of machine learning methods based on artificial neural networks with representation learning. Learning can be supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised.
De ...
and Machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
algorithm to accurately diagnose the disease.
Differential diagnosis
Recognizing IPF in clinical practice can be challenging assymptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an disease, illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormali ...
often appear similar to those of more common diseases, such as asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce ...
(COPD) and congestive heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
www.diagnoseipf.com
. The key issue facing clinicians is whether the presenting history,
symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an disease, illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormali ...
(or signs), radiology
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiat ...
, and pulmonary function testing
Pulmonary function testing (PFT) is a complete evaluation of the respiratory system including patient history, physical examinations, and tests of pulmonary function. The primary purpose of pulmonary function testing is to identify the severity ...
are collectively in keeping with the diagnosis of IPF or whether the findings are due to another process. It has long been recognized that patients with ILD related to asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
exposure, drugs
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalat ...
(such as chemotherapeutic
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemothera ...
agents or nitrofurantoin
Nitrofurantoin is an antibacterial medication used to treat urinary tract infections, but it is not as effective for kidney infections. It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include nausea, loss of appetite, diarrhea, and headaches. Rarely ...
), rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involv ...
and scleroderma
Scleroderma is a group of autoimmune diseases that may result in changes to the skin, blood vessels, muscles, and internal organs. The disease can be either localized to the skin or involve other organs, as well. Symptoms may include areas ...
/systemic sclerosis
Systemic scleroderma, or systemic sclerosis, is an autoimmune rheumatic disease characterised by excessive production and accumulation of collagen, called fibrosis, in the skin and internal organs and by injuries to small arteries. There are two ...
may be difficult to distinguish from IPF. Other differential diagnostic considerations include interstitial lung disease related to mixed connective tissue disease
Mixed connective tissue disease, commonly abbreviated as MCTD, is an autoimmune disease characterized by the presence of elevated blood levels of a specific autoantibody, now called anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) together with a mix of symptoms of ...
, advanced sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly af ...
, chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird dropping ...
, pulmonary Langerhan's cell histiocytosis and radiation-induced lung injury
Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is a general term for damage to the lungs as a result of exposure to ionizing radiation. In general terms, such damage is divided into early inflammatory damage (''radiation pneumonitis'') and later complicatio ...
.
Classification
 Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) belongs to a large group of more than 200 lung diseases known as
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) belongs to a large group of more than 200 lung diseases known as interstitial lung disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the alveoli (air sacs)) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmo ...
s (ILDs), which are characterized by the involvement of the lung interstitium, the tissue between the air sacs of the lung. IPF is one specific presentation of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia
Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), or noninfectious pneumonia are a class of diffuse lung diseases. These diseases typically affect the pulmonary interstitium, although some also have a component affecting the airways (for instance, cryptoge ...
(IIP), which is in turn a type of ILD, also known as diffuse parenchymal lung disease
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the alveoli (air sacs)) of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pu ...
(DPLD).
The 2002 American Thoracic Society The American Thoracic Society (ATS) is a nonprofit organization focused on improving care for pulmonary diseases, critical illnesses and sleep-related breathing disorders. It was established in 1905 as the
American Sanatorium Association, and ch ...
/European Respiratory Society
The European Respiratory Society, or ERS, is a non-profit organization with offices in Lausanne, Brussels and Sheffield. It was founded in 1990 in the field of respiratory medicine. The organization was formed with the merger of the Societas Euro ...
(ATS/ERS) classification of IIPs was updated in 2013. In this new classification there are three main categories of idiopathic
An idiopathic disease is any disease with an unknown cause or mechanism of apparent wikt:spontaneous, spontaneous origin. From Ancient Greek, Greek ἴδιος ''idios'' "one's own" and πάθος ''pathos'' "suffering", ''idiopathy'' means approxi ...
interstitial pneumonias (IIPs): major IIPs, rare IIPs, and unclassifiable IIPs. The major IIPs are grouped into chronic fibrosing IPs (this includes IPF and non-specific interstitial pneumonia
Non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) is a form of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia.
Symptoms
Symptoms include cough, difficulty breathing, and fatigue.
Causes
It has been suggested that idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia has a ...
SIP; smoking-related IPs (i.e. respiratory bronchiolitis–interstitial lung disease B-ILDand desquamative interstitial pneumonia IP; and acute/subacute IPs (i.e. cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP), formerly known as bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), is an inflammation of the bronchioles ( bronchiolitis) and surrounding tissue in the lungs. It is a form of idiopathic interstitial pn ...
OPand acute interstitial pneumonia
Acute interstitial pneumonitis is a rare, severe lung disease that usually affects otherwise healthy individuals. There is no known cause or cure.
Acute interstitial pneumonitis is often categorized as both an interstitial lung disease and a form ...
IP.
The diagnosis of IIPs requires exclusion of known causes of ILD. Examples of ILD of known cause include hypersensitivity pneumonitis
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis (HP) or extrinsic allergic alveolitis (EAA) is a syndrome caused by the repetitive inhalation of antigens from the environment in susceptible or sensitized people. Common antigens include molds, bacteria, bird dropping ...
, pulmonary Langerhan's cell histiocytosis, asbestosis
Asbestosis is long-term inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis, scarring of the human lung, lungs due to asbestos, asbestos fibers. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and chest pain, chest tightness. Complications may include ...
, and collagen vascular disease
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds togeth ...
. However, these disorders frequently affect not only the interstitium, but also the airspaces, peripheral airways, and blood vessels.
Radiology
Chest X-rays
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a Projectional radiography, projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most ...
are useful in the follow up routine of IPF patients. Plain chest X-rays are unfortunately not diagnostic but may reveal decreased lung volumes
Lung volumes and lung capacities refer to the volume of air in the lungs at different phases of the respiratory cycle.
The average total lung capacity of an adult human male is about 6 litres of air.
Tidal breathing is normal, resting breath ...
, typically with prominent reticular interstitial markings near the lung bases.  The radiological evaluation through HRCT is an essential point in the diagnostic pathway in IPF. HRCT is performed using a conventional computed axial tomographic scanner without injection of contrast agents. Evaluation slices are very thin, 1–2 mm.
Typical HRCT of the chest of IPF demonstrates fibrotic changes in both lungs, with a predilection for the bases and the periphery. According to the joint ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT 2011 guidelines, HRCT is an essential component of the diagnostic pathway in IPF which can identify UIP by the presence of:
* Reticular opacities, often associated with traction bronchiectasis
*
The radiological evaluation through HRCT is an essential point in the diagnostic pathway in IPF. HRCT is performed using a conventional computed axial tomographic scanner without injection of contrast agents. Evaluation slices are very thin, 1–2 mm.
Typical HRCT of the chest of IPF demonstrates fibrotic changes in both lungs, with a predilection for the bases and the periphery. According to the joint ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT 2011 guidelines, HRCT is an essential component of the diagnostic pathway in IPF which can identify UIP by the presence of:
* Reticular opacities, often associated with traction bronchiectasis
* Honeycombing
Honeycombing or "honeycomb lung" is the radiological appearance seen with widespread fibrosis and is defined by the presence of small cystic spaces with irregularly thickened walls composed of fibrous tissue
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibr ...
manifested as cluster cystic airspaces, typically of comparable diameters (3–10 mm) but occasionally large. Usually sub-pleural and characterized by well-defined walls and disposed in at least two lines. Generally one line of cysts is not sufficient to define honeycombing
* Ground-glass opacities
Ground-glass opacity (GGO) is a finding seen on chest x-ray (radiograph) or computed tomography (CT) imaging of the lungs. It is typically defined as an area of hazy opacification (x-ray) or increased attenuation (CT) due to air displacement ...
are common but less extensive than the reticulation
* Distribution characteristically basal and peripheral though often patchy.

Histology
According to the updated 2011 guidelines, in the absence of a typical UIP pattern on HRCT, a surgical lung biopsy is required for confident diagnosis. Histologic specimens for the diagnosis of IPF must be taken at least in three different places and be large enough that the pathologist can comment on the underlying lung architecture. Small biopsies, such as those obtained via transbronchial lungbiopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a diseas ...
(performed during bronchoscopy) are usually not sufficient for this purpose. Hence, larger biopsies obtained surgically via a thoracotomy
A thoracotomy is a surgical procedure to gain access into the pleural space of the chest. It is performed by surgeons (emergency physicians or paramedics under certain circumstances) to gain access to the thoracic organs, most commonly the hea ...
or thoracoscopy
Thoracoscopy is a medical procedure involving internal examination, biopsy and/or resection/drainage of disease or masses within the pleural cavity, usually with video assistance. Thoracoscopy may be performed either under general anaesthe ...
are usually necessary.
Lung tissue from people with IPF usually show a characteristic histopathologic UIP pattern and is therefore the pathologic counterpart of IPF. Although a pathologic diagnosis of UIP often corresponds to a clinical diagnosis of IPF, a UIP histologic pattern can be seen in other diseases as well, and fibrosis of known origin (rheumatic diseases for example). There are four key features of UIP including interstitial fibrosis in a 'patchwork pattern', interstitial scarring, honeycomb changes and fibroblast foci.
Fibroblastic foci are dense collections of myofibroblasts and scar tissue and, together with honeycombing, are the main pathological findings that allow a diagnosis of UIP.

Bronchoalveolar lavage
Bronchoalveolar lavage
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) (also known as bronchoalveolar washing) is a diagnostic method of the lower respiratory system in which a bronchoscope is passed through the mouth or nose into an appropriate airway in the lungs, with a measured amoun ...
(BAL) is a well-tolerated diagnostic procedure in ILD. BAL cytology analyses (differential cell counts) should be considered in the evaluation of patients with IPF at the discretion of the treating physician based on availability and experience at their institution. BAL may reveal alternative specific diagnoses: malignancy
Malignancy () is the tendency of a medical condition to become progressively worse.
Malignancy is most familiar as a characterization of cancer. A ''malignant'' tumor contrasts with a non-cancerous ''benign'' tumor in that a malignancy is not s ...
, infections
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmiss ...
, eosinophilic pneumonia
Eosinophilic pneumonia is a disease in which an eosinophil, a type of white blood cell, accumulates in the lungs. These cells cause disruption of the normal air spaces (alveoli) where oxygen is extracted from the atmosphere. Several different kin ...
, histiocytosis X, or alveolar proteinosis
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare lung disorder characterized by an abnormal accumulation of surfactant-derived lipoprotein compounds within the alveoli of the lung. The accumulated substances interfere with the normal gas exchange and ...
. In the evaluation of patients with suspected IPF, the most important application of BAL is in the exclusion of other diagnoses. Prominent lymphocytosis
Lymphocytosis is an increase in the number or proportion of lymphocytes in the blood. Absolute lymphocytosis is the condition where there is an increase in the lymphocyte count beyond the normal range while relative lymphocytosis refers to the cond ...
(>30%) generally allows excluding a diagnosis of IPF.
Pulmonary function tests
Spirometry classically reveals a reduction in thevital capacity
Vital capacity (VC) is the maximum amount of air a person can inhale after a maximum exhalation. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and expiratory reserve volume. It is approximately equal to Forced Vital Capacity ( ...
(VC) with either a proportionate reduction in airflows, or increased airflows for the observed vital capacity. The latter finding reflects the increased lung stiffness (reduced lung compliance) associated with pulmonary fibrosis, which leads to increased lung elastic recoil.
Measurement of static lung volumes using body plethysmography
A plethysmograph is an instrument for measuring changes in volume within an organ or whole body (usually resulting from fluctuations in the amount of blood or air it contains). The word is derived from the Greek "plethysmos" (increasing, enla ...
or other techniques typically reveals reduced lung volumes (restriction). This reflects the difficulty encountered in inflating the fibrotic lungs.
The diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) is invariably reduced in IPF and may be the only abnormality in mild or early disease. Its impairment underlies the propensity of patients with IPF to exhibit oxygen desaturation with exercise which can also be evaluated using the 6-minute walk test (6MWT).
Terms such as 'mild', 'moderate', and 'severe' are sometimes used for staging disease and are commonly based on resting pulmonary function test measurements. However, there is no clear consensus regarding the staging of IPF patients and what are the best criteria and values to use. Mild-to-moderate IPF has been characterized by the following functional criteria:
* Forced vital capacity
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is he ...
(FVC) of ≥50%
* DLCO of ≥30%
* 6MWT distance ≥150 meters.
Treatment
The goals of treatment in IPF are essentially to reduce the symptoms, stop disease progression, prevent acute exacerbations, and prolong survival. Preventive care (e.g. vaccinations) and symptom-based treatment should be started early in every patient.Oxygen therapy
In the 2011 IPF guidelines,oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy, also known as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as medical treatment. Acute indications for therapy include hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels), carbon monoxide toxicity and cluster headache. It may also be prophylactica ...
, or supplementary oxygen for home use, became a strong recommendation for use in those patients with significantly low oxygen levels at rest. Although oxygen therapy has not been shown to improve survival in IPF, some data indicate an improvement in exercise capacity.
Pulmonary rehabilitation
Fatigue and loss of muscular mass are common and disabling problems for patients with IPF.Pulmonary rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation, also known as respiratory rehabilitation, is an important part of the management and health maintenance of people with chronic respiratory disease who remain symptomatic or continue to have decreased function despite stand ...
may alleviate the overt symptoms of IPF and improve functional status by stabilizing and/or reversing the extrapulmonary features of the disease. The number of published studies on the role of pulmonary rehabilitation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is small, but most of these studies have found significant short-term improvements in functional exercise tolerance, quality of life, and dyspnea on exertion. Typical programs of rehabilitation include exercise training, nutritional modulation, occupational therapy, education and psychosocial counseling. In the late phase of disease, IPF patients tend to discontinue physical activity due to increasing dyspnea. Whenever possible, this should be discouraged.
Medications
A number of treatments have been investigated in the past for IPF, including interferon gamma-1β,bosentan
Bosentan, sold under the brand name Tracleer and Safebo among others, is a dual endothelin receptor antagonist medication used in the treatment of pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH).
Bosentan is available as film-coated tablets (62.5 mg o ...
, ambrisentan
Ambrisentan (U.S. trade name Letairis; E.U. trade name Volibris; India trade name Pulmonext by MSN labs) is a drug indicated for use in the treatment of pulmonary hypertension.
The peptide endothelin constricts muscles in blood vessels, incr ...
, and anticoagulants
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where the ...
, but these are no longer considered effective treatment options. Many of these earlier studies were based on the hypothesis that IPF is an inflammatory disorder.
Pirfenidone
ACochrane review
Cochrane (previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration) is a British international charitable organisation formed to organise medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professi ...
comparing pirfenidone
Pirfenidone is a medication used for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. It works by reducing lung fibrosis through downregulation of the production of growth factors and procollagens I and II.
It was first approved in Japan for t ...
with placebo, found a reduced risk of disease progression by 30%. FVC or VC was also improved, even if a mild slowing in FVC decline could be demonstrated only in one of the two CAPACITY trials. A third study, which was completed in 2014 found reduced decline in lung function and IPF disease progression. The data from the ASCEND study were also pooled with data from the two CAPACITY studies in a pre-specified analysis which showed that pirfenidone reduced the risk of death by almost 50% over one year of treatment.
N-acetylcysteine and triple therapy
''N''-Acetylcysteine (NAC) is a precursor to glutathione, anantioxidant
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation, a chemical reaction that can produce free radicals. This can lead to polymerization and other chain reactions. They are frequently added to industrial products, such as fuels and lubricant ...
. It has been hypothesized that treatment with high doses of NAC may repair an oxidant–antioxidant imbalance that occurs in the lung tissue of patients with IPF. In the first clinical trial of 180 patients (IFIGENIA), NAC was shown in previous study to reduce the decline in VC and DLCO over 12 months of follow-up when used in combination with prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium ...
and azathioprine
Azathioprine (AZA), sold under the brand name Imuran, among others, is an immunosuppressive medication. It is used in rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and systemic lupus erythematosus, ...
(triple therapy).
More recently, a large randomized, controlled trial (PANTHER-IPF) was undertaken by the National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
(NIH) in the US to evaluate triple therapy and NAC monotherapy in IPF patients. This study found that the combination of prednisone, azathioprine, and NAC increased the risk of death and hospitalizations and the NIH announced in 2012 that the triple-therapy arm of the PANTHER-IPF study had been terminated early.
This study also evaluated NAC alone and the results for this arm of the study were published in May 2014 in the ''New England Journal of Medicine
''The New England Journal of Medicine'' (''NEJM'') is a weekly medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. It is among the most prestigious peer-reviewed medical journals as well as the oldest continuously published one.
Hist ...
'', concluding that "as compared with placebo, acetylcysteine offered no significant benefit with respect to the preservation of FVC in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with mild-to-moderate impairment in lung function".
Nintedanib
Nintedanib
Nintedanib, sold under the brand names Ofev and Vargatef, is an oral medication used for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and along with other medications for some types of non-small-cell lung cancer.
In March 2020, it was appro ...
is a triple angiokinase inhibitor that targets receptor tyrosine kinase
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are the high-affinity cell surface receptors for many polypeptide growth factors, cytokines, and hormones. Of the 90 unique tyrosine kinase genes identified in the human genome, 58 encode receptor tyrosine kinase ...
s involved in the regulation of angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature by processes of sprouting and splitting ...
: fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), platelet-derived growth factor receptor
Platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGF-R) are cell surface tyrosine kinase receptors for members of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) family. PDGF subunits -A and -B are important factors regulating cell proliferation, cellu ...
(PDGFR), and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
VEGF receptors are receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). There are three main subtypes of VEGFR, numbered 1, 2 and 3. Also, they may be membrane-bound (mbVEGFR) or soluble (sVEGFR), depending on alternative splicing.
Inh ...
(VEGFR), which have also been implicated in the pathogenesis of fibrosis and IPF. In both phase III trials, nintedanib reduced the decline in lung function by approximately 50% over one year. It was approved by the US FDA in October 2014 and authorised in Europe in January 2015.
Lung transplantation
Lung transplantation
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one lung lobe. ...
may be suitable for those patients physically eligible to undergo a major transplant operation. In IPF patients, lung transplant has been shown to reduce the risk of death by 75% as compared with patients who remain on the waiting list. Since the introduction of the lung allocation score (LAS), which prioritizes transplant candidates based on survival probability, IPF has become the most common indication for lung transplantation in the USA.
Symptomatic patients with IPF younger than 65 years of age and with a body mass index (BMI) ≤26 kg/m2 should be referred for lung transplantation, but there are no clear data to guide the precise timing for LTx. Although controversial, the most recent data suggest that bilateral lung transplantation is superior to single lung transplantation in patients with IPF. Five-year survival rates after lung transplantation in IPF are estimated at between 50 and 56%.
Palliative care
Palliative care
Palliative care (derived from the Latin root , or 'to cloak') is an interdisciplinary medical caregiving approach aimed at optimizing quality of life and mitigating suffering among people with serious, complex, and often terminal illnesses. Wit ...
focuses on reducing symptoms and improving the comfort of patients rather than treating the disease. This may include treatment of worsening symptoms with the use of chronic opioids
Opioids are substances that act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use ...
for severe dyspnea and cough. Further, oxygen therapy may be useful for palliation of dyspnea in hypoxemic patients.
Palliative care also includes relief of physical and emotional suffering and psychosocial support for patients and caregivers. With disease progression, patients may experience fear, anxiety and depression and psychological counseling should therefore be considered. In a recent study of outpatients with ILDs, including IPF, depression score, functional status (as assessed by walk test), as well as pulmonary function, all contributed to the severity of dyspnea.
In selected cases of particularly severe dyspnea morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make ...
could be considered. It can reduce dyspnea, anxiety and cough without significant decrease in oxygen saturation.
Follow-up
IPF is often misdiagnosed, at least until physiological and/or imaging data suggest the presence of an ILD leading to delay in accessing appropriate care. Considering that IPF is a disease with a median survival of three years after diagnosis, early referral to a center with specific expertise should therefore be considered for any patient with suspected or known ILD. On the basis of the complex differential diagnostic, multidisciplinary discussion between pulmonologists, radiologists, and pathologists experienced in the diagnosis of ILD is of the utmost importance to an accurate diagnosis. Those with IPF have higher chances of getting lung cancer, at a rate of 13.5% where the most common cancer type isSquamous-cell carcinoma of the lung
Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC) of the lung is a histologic type of non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). It is the second most prevalent type of lung cancer after lung adenocarcinoma and it originates in the bronchi. Its tumor cells are characteriz ...
. a routine evaluation every 3 to 6 months, including spirometry (body plethysmography), diffusion capacity testing, chest X-rays, 6MWT, assessment of dyspnea, quality of life, oxygen requirement is mandatory.
In addition, the increasing awareness of complications and common concomitant conditions frequently associated with IPF requires a routinely evaluation of comorbidities, most of them simply reflecting concurrent diseases of aging, and medications with their interaction and side effects.
Acute exacerbations
Acute exacerbations of IPF (AE-IPF) are defined as an unexplained worsening or development of dyspnea within 30 days with new radiological infiltrates at HRCT abnormality often superimposed on a background consistent with UIP pattern. The yearly incidence of AE-IPF is between 10 and 15% of all patients. The prognosis of AE-IPF is poor, with mortality ranging from 78% to 96%. Other causes of AE-IPF such as pulmonary embolism, congestive heart failure, pneumothorax, or infection need to be excluded. Pulmonary infection have to be ruled out by endotracheal aspirate or BAL. Many patients experiencing acute deterioration require intensive care treatment, particularly when respiratory failure is associated with hemodynamic instability, significant comorbidities or severe hypoxemia. However, mortality during hospitalization is high. Mechanical ventilation should be introduced only after carefully weighing the person's long-term prognosis and, whenever possible, the person's wishes. However, current guidelines discourage the use of mechanical ventilation in patients with respiratory failure secondary to IPF.Prognosis
 The clinical course of IPF can be unpredictable. IPF progression is associated with an estimated median survival time of 2 to 5 years following diagnosis.
The 5-year survival for IPF ranges between 20 and 40%, a mortality rate higher than that of a number of malignancies, including colon cancer, multiple myeloma and bladder cancer.
Recently a multidimensional index and staging system has been proposed to predict mortality in IPF. The name of the index is GAP and is based on gender age and two lung physiology variables (FVC and DLCO that are commonly measured in clinical practice to predict mortality in IPF. The highest stage of GAP (stage III) has been found to be associated with a 39% risk of mortality at 1 year. This model has also been evaluated in IPF and other ILDs and shown good performance in predicting mortality in all main ILD subtypes. A modified ILD-GAP Index has been developed for application across ILD subtypes to provide disease-specific survival estimates. In IPF patients, the overall mortality at 5 years rate is high but the annual rate of all-cause mortality in patients with mild to moderate lung impairment is relatively low. This is the reason why change in lung function (FVC) is usually measured in 1-year clinical trials of IPF treatments rather than survival.
In addition to clinical and physiological parameters to predict how rapidly patients with IPF might progress, genetic and molecular features are also associated with IPF mortality. For example, it has been shown that IPF patients who have a specific genotype in the mucin MUC5B gene polymorphism (see above) experience slower decline in FVC and significantly improved survival. Even if such data are interesting from a scientific point of view, the application in the clinical routine of a prognostic model based on specific genotypes is still not possible.
The clinical course of IPF can be unpredictable. IPF progression is associated with an estimated median survival time of 2 to 5 years following diagnosis.
The 5-year survival for IPF ranges between 20 and 40%, a mortality rate higher than that of a number of malignancies, including colon cancer, multiple myeloma and bladder cancer.
Recently a multidimensional index and staging system has been proposed to predict mortality in IPF. The name of the index is GAP and is based on gender age and two lung physiology variables (FVC and DLCO that are commonly measured in clinical practice to predict mortality in IPF. The highest stage of GAP (stage III) has been found to be associated with a 39% risk of mortality at 1 year. This model has also been evaluated in IPF and other ILDs and shown good performance in predicting mortality in all main ILD subtypes. A modified ILD-GAP Index has been developed for application across ILD subtypes to provide disease-specific survival estimates. In IPF patients, the overall mortality at 5 years rate is high but the annual rate of all-cause mortality in patients with mild to moderate lung impairment is relatively low. This is the reason why change in lung function (FVC) is usually measured in 1-year clinical trials of IPF treatments rather than survival.
In addition to clinical and physiological parameters to predict how rapidly patients with IPF might progress, genetic and molecular features are also associated with IPF mortality. For example, it has been shown that IPF patients who have a specific genotype in the mucin MUC5B gene polymorphism (see above) experience slower decline in FVC and significantly improved survival. Even if such data are interesting from a scientific point of view, the application in the clinical routine of a prognostic model based on specific genotypes is still not possible.
Epidemiology
Although rare, IPF is the most common form of IIP. The prevalence of IPF has been estimated between 14.0 and 42.7 per 100,000 persons based on a USA analysis of healthcare claims data, with variation depending on the case definitions used in this analyses.Pulmonary Fibrosis Foundation. "Prevalence and Incidence". Pulmonaryfibrosis.org. Retrieved 11 April 2013 IPF is more common in men than in women and is usually diagnosed in people over 50 years of age. The incidence of IPF is difficult to determine as uniform diagnostic criteria have not been applied consistently. A recent study from the USA estimated the incidence of IPF to be between 6.8 and 16.3 per 100,000 persons. In the 27 European Union countries, a range of sources estimate an incidence of 4.6–7.4 people per 100,000 of the population, suggesting that approximately 30,000–35,000 new patients will be diagnosed with IPF each year. A recent single-centre, retrospective, observational cohort study including incident patients diagnosed with ILD at Aarhus University Hospital (Denmark) between 2003 and 2009 revealed an incidence of 4.1 per 100,000 inhabitants/year for ILD. IPF was the most common diagnosis (28%) followed by connective tissue disease-related ILD (14%), hypersensitivity pneumonitis (7%) and non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) (7%). IPF incidence was 1.3 per 100,000 inhabitants/year. Due to a heterogeneous distribution of the disease across European countries, epidemiological data needs to be updated through a Europe-wide registry for ILD and IPF.Other animals
IPF has been recognized in several breeds of both dogs and cats, and has been best characterized inWest Highland White Terriers
The West Highland White Terrier, commonly known as the Westie, is a dog breed, breed of dog from Scotland with a distinctive white harsh coat with a somewhat soft white undercoat. It is a medium-sized terrier, although with longer legs than ...
. Veterinary patients with the condition share many of the same clinical signs as their human counterparts, including progressive exercise intolerance, increased respiratory rate, and eventual respiratory distress.
Prognosis is generally poor.
Research
A number of agents are currently being investigated inPhase II clinical trial
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases ...
s for IPF, including the monoclonal antibodies simtuzumab, tralokinumab
Tralokinumab sold under the brand names Adtralza (EU/UK) and Adbry (US) among others, is a human monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Tralokinumab targets the cytokine interleukin 13.
The most common side effects in ...
, lebrikizumab
Lebrikizumab ( INN) is a humanized monoclonal antibody and an experimental immunosuppressive drug for the treatment of asthma that cannot be adequately controlled with inhalable glucocorticoids. The drug was created by Tanox under the name ''TNX ...
and FG-3019, a lysophosphatidic acid
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) is a phospholipid derivative that can act as a signaling molecule.
Function
LPA acts as a potent mitogen due to its activation of three high-affinity G-protein-coupled receptors called LPAR1, LPAR2, and LPAR3 (a ...
receptor antagonist (BMS-986020). A Phase II study of STX-100 is also ongoing. These molecules are directed against several growth factors and cytokines that are known to play a role in the proliferation, activation, differentiation or inappropriate survival of fibroblasts.
mir-29 microRNA precursor
The miR-29 microRNA precursor, or pre-miRNA, is a small RNA molecule in the shape of a stem-loop or hairpin. Each arm of the hairpin can be processed into one member of a closely related family of short non-coding RNAs that are involved in regul ...
investigations in mice have produced reversal of induced IPF. MRG-201 is currently being tested as-of 2016, but not in IPF patients yet, and no human trials for IPF use have been scheduled .
Stem cell therapies for IPF are an area of research.
A machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
algorithm has been proposed that discovers subtle patterns in individual history of medical encounters to reliably estimate the risk of a future IPF diagnosis, up to four years before current medical practice. The algorithm outputs a score (ZCoR) using medical history on file with no new tests, and might be deployable as a universal IPF screening tool in primary care. ZCoR has been trained and validated on nearly 3 million patients across multiple databases, achieving high predictive performance in out-of-sample data (positive likelihood ratio > 30 with 99% specificity). The authors conclude that past respiratory disorders maximally contribute to IPF risk, followed by known IPF comorbidities, metabolic diseases, cardiovascular abnormalities, and diseases of the eye, with the overall pattern of the importance ranking substantially invariant across the sexes.
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Respiratory diseases principally affecting the interstitium Idiopathic diseases Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate